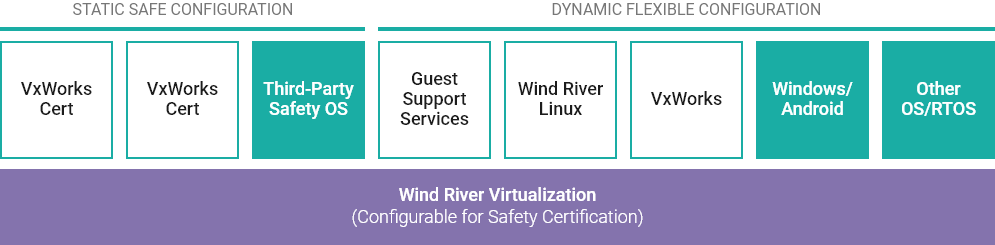
A hypervisor is software that uses virtualization technology to create, run, and manage virtual machines (VMs). Also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), a hypervisor keeps its operating system and resources isolated from the virtual machines it manages.
A key benefit of hypervisors is that multiple operating systems with very different characteristics can run at the same time, next to each other, and they can share the same virtualized hardware resources. Without this capability, only one operating system can be run on a computer hardware system.
Benefits of Hypervisors
Data Replication and Cloning
Cloning and replicating virtual machines is a difficult task. Using a hypervisor to clone or replicate a virtual machine is much easier and more cost-effective than using the original storage-based replication method, which requires replicating the full volume of all the virtual machines on the server and would require a huge amount of storage space.
Replication or cloning with a hypervisor is simple. You can choose the VMs and the components to be replicated, rather than all the VMs, which allows you to save storage space on the servers. Hardware-neutral hypervisor-based replication lets you take any data duplicates and move and store them easily in any storage device.
Consolidating Servers
Inbuilt graphical dashboards are components of hypervisors. Additional enhancements to inbuilt dashboards provide better visibility, which in turn provides the ability to centrally consolidate and manage servers. This can be accomplished even though the VMs can each be running different operating systems.
Industrial Control Automation Consolidation
With the use of a hypervisor and VMs, an industrial control automation system manufacturer can take previously separate computerized components of control automation system equipment and consolidate them on a single embedded system platform.
Test Environments
A hypervisor can create virtual systems that can test systems and applications as they are under development. This makes it easier to verify whether coding and system operations work properly.
Desktop Virtualization
With a hypervisor, a server can host a client’s or worker’s virtual desktop, which replicates the worker’s physical desktop and can be used over the internet.
Benefits of Hypervisors
An embedded hypervisor is designed to support embedded systems needs and requirements. It is usually a Type 1 hypervisor that is targeted to support the virtual requirements of embedded systems within a device, not IT servers or desktop computers. An embedded hypervisor’s overall software coding size is small and provides real-time or fast hypervisor capabilities with support for multiple isolated VMs in an embedded system device.
Due to its size and requirements, an embedded hypervisor is designed to minimally affect the system resources on the device and to support real-time latency. This type of hypervisor can implement scheduling policies between the different virtual machines and deliver support to the components of a real-time system for an embedded device.